KUALA LUMPUR (Dec 27): The proposed adjustment in Peninsular Malaysia’s base electricity tariff under the Regulatory Period 2025-2027 (RP4) is mainly a “rebasing exercise” to reflect higher fuel costs assumption, said Tenaga Nasional Bhd (KL:TENAGA).
Amid expectations of high costs of coal and gas, the government is also “putting a lot of thought” in the review of the existing tariff structure to protect vulnerable groups and ensure affordability, said the national utility company.
“The revision of the base tariff is mainly to reflect the market fuel prices,” said Tenaga chief financial officer Datuk Nazmi Othman at a media briefing on the RP4 adjustment. The government decides on the tariffs, and fuel prices adjustment is neutral to Tenaga, Nazmi said.
He added that in line with current government policy, the tariff structure will be formalised in a way not to burden the majority of the population.
How electricity tariffs are set in Malaysia
Under the 'incentive-based regulation', the base tariff is reviewed every regulatory period lasting three years which takes into account potential spending required to expand or maintain the grid.
Base electricity tariff comprises network and retail costs at around 30%, with the balance 70% made up of generation costs, which include fuel costs as well as capacity charges for power plants.
The base electricity tariff is an average across all users. Actual tariffs are imposed at different rates, depending on consumption trend and the user category — such as households, as well as low-, medium- and high-voltage commercial and industrial customers.
The final tariff to be paid by consumers are adjusted every six months under the regulation’s imbalance cost pass-through mechanism in the form of rebates or surcharge on top of the base tariff.
If fuel costs exceed the projection, a surcharge will be levied resulting in higher tariffs for the consumers, while a rebate will lower the final tariffs if fuel costs drop below forecasts.
Currently, electricity users are paying more than the current base tariffs. In short, the fuel costs forecasted in RP3 (2022-2024) had been lower than market prices, resulting in the surcharge having to be imposed.
Final tariffs still being reviewed
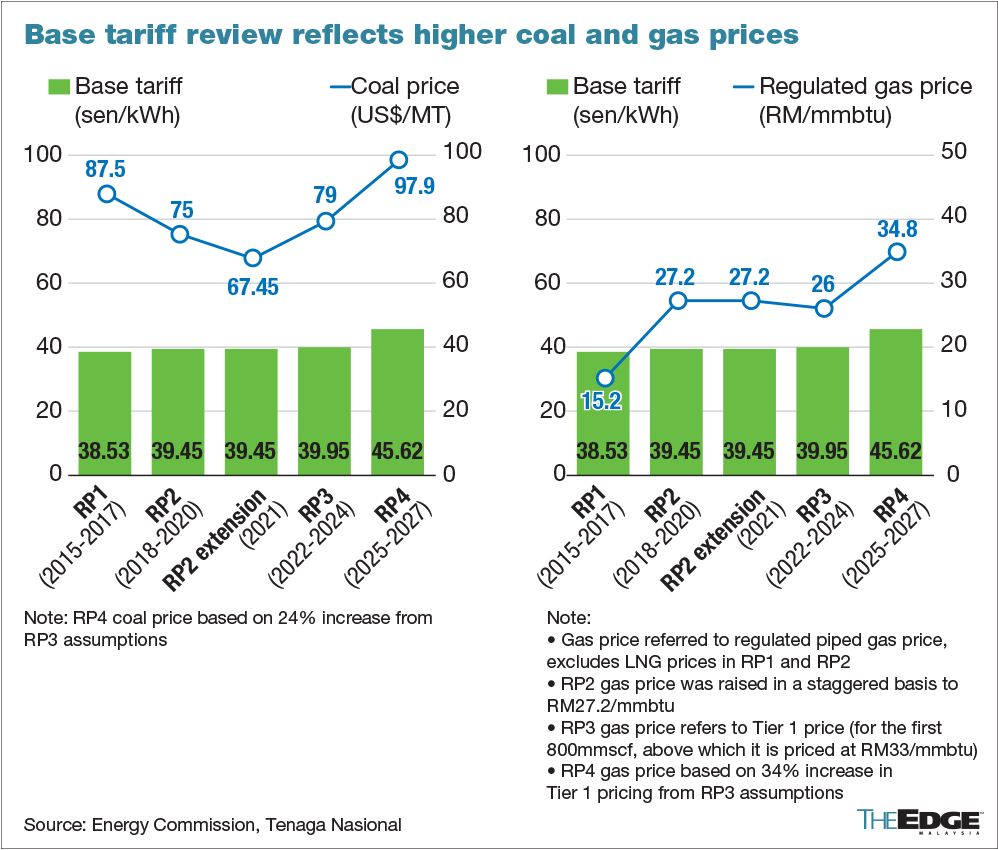
Under RP4 (2025-2027), Tenaga has revealed base electricity tariff will be adjusted to 45.62 sen/kWh, from 39.95 sen/kWh. As the government is still reviewing the tariff structure, the base tariff “could be lower or higher depending on the prevailing market forces”, said Nazmi, and this was affirmed by Energy Commission chief executive officer Datuk Abdul Razib Dawood, who was present at the briefing.
The 14.2% increase is largely on the back of a 24% increase in the forecasted three-year average price of coal from US$79 (RM353.86) per tonne, and 34% increase in forecasted gas prices from RM26-RM33 per million British thermal units (mmbtu).
Following the post-pandemic commodity price shocks — which saw coal prices rising to over US$400 per tonne — the commodity has stabilised to US$125 per tonne, from US$50 per tonne just five years ago.
A 24% increase in RP3 coal prices amounts to US$97.96 per tonne, while a 34% increase in RP3 gas prices amounts to RM34-RM44/mmbtu, compared with Malaysia's benchmark piped gas price of RM42.13/mmbtu in the fourth quarter of 2024.
Tenaga, Nazmi said, could secure coal supply for the next three years through long-term contracts, but the pricing is closer to spot pricing due to tight market supply as governments revisit coal-generated power for security of supply.
Meanwhile, bulk of the piped natural gas supplied to the power sector (800 million standard cubic feet) by Petroliam Nasional Bhd is currently sold at a discount of more than 10% to global market prices, a legacy practice that needs to be revisited amid increased reliance on imported liquefied natural gas, which needs to be bought at market prices. The remaining 200-300 million standard cubic feet consumed by the power sector is marked to market prices.
For now, effective electricity tariffs remain unchanged in the first half of 2025.
'Contingent' capex in RP4 not included in base tariffs
At the briefing, Nazmi also clarified that the jump in approved capital expenditure (capex) for the transmission and distribution (T&D) segment is not all incorporated into the base tariffs, or ploughed back from the public.
Of the RM42.82 billion approved capex for RP4, about RM26.5 billion is base capex for ‘business-as-usual’ infrastructure expansion, up from RM20.55 billion in RP3 (2022-2024). These are ploughed back through the base electricity tariffs.
The balance, north of RM16 billion, is “contingent” capex for energy transition-related T&D network upgrades, depending on grid stability and subject to further approvals. This is not part of the base tariff, Nazmi said.
This includes efforts to address solar intermittency, and smart grid investments, as well as establishing networks for new industrial zones, for example, he added.
On the rate of return (or weighted average cost of capital) of 7.3% allowed on Tenaga’s T&D assets, Nazmi said Tenaga lauded the government’s decision to keep the rates unchanged since the start of RP2 in 2018.
“That will enable us to invest [with] fair and reasonable returns to build more infrastructure to ensure reliability and sustainability of the power industry,” Nazmi noted.